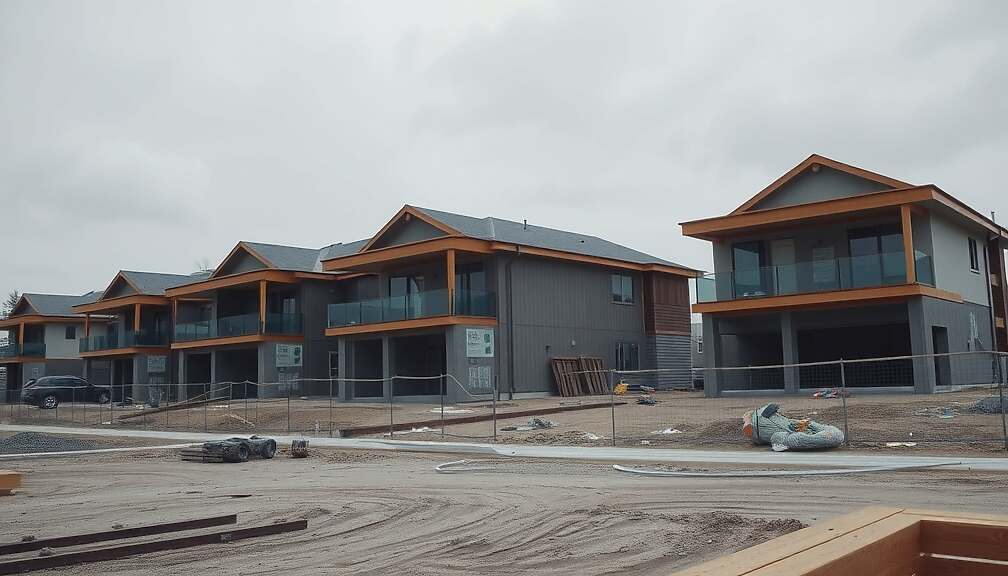
Instone, a publicly traded project developer, is signaling a significant shift in the German real estate market with a renewed focus on residential construction following years of crisis. The company’s largest undertaking to date centers around the Benrather Gärten in Düsseldorf, a sprawling 15-hectare site acquired from the financially troubled Adler Group.
According to a statement in the “Handelsblatt”, CEO Kruno Crepulja outlined ambitious plans for the former steel factory site, envisioning 800 to 1,000 apartments targeted towards the middle class, with a total project volume estimated between €450 and €500 million. This acquisition is part of a series of recent additions to Instone’s portfolio, further bolstered by projects in Nuremberg (160 condominiums in the Luitpold-Viertel) and Leipzig (162 apartments in the Löwitz-Quartier).
Crepulja expressed optimism regarding market recovery, citing substantial investor interest. He noted a demand exceeding even the peaks of the previous real estate boom, largely attributable to the appealing tax depreciation options introduced by the 2024 Growth Opportunities Act. This legislation, he argued, creates a particularly attractive investment climate, allowing high-income earners to significantly reduce their tax burden.
The company also claims to be benefiting from advantageous construction costs, reportedly ranging from €3,500 to €4,000 per square meter including land acquisition and construction costs kept below €3,000 per square meter adhering to the QNG-40 standard. This apparent cost-effectiveness, coupled with the favorable tax environment, raises questions about the widening gap between accessibility to affordable housing and the financial incentives driving large-scale investments. Critics suggest that while such projects may stimulate economic activity, the preferential tax treatment skewed towards affluent investors undermines efforts to address the pressing need for genuinely affordable housing options for lower and middle-income families. The rapid recovery of the real estate sector, fuelled by these incentives, also warrants scrutiny regarding potential for inflationary pressures and a reinforcement of existing socio-economic disparities.